Κατανόηση των Βιομηχανικών Αποβλήτων: Τύποι και Πηγές
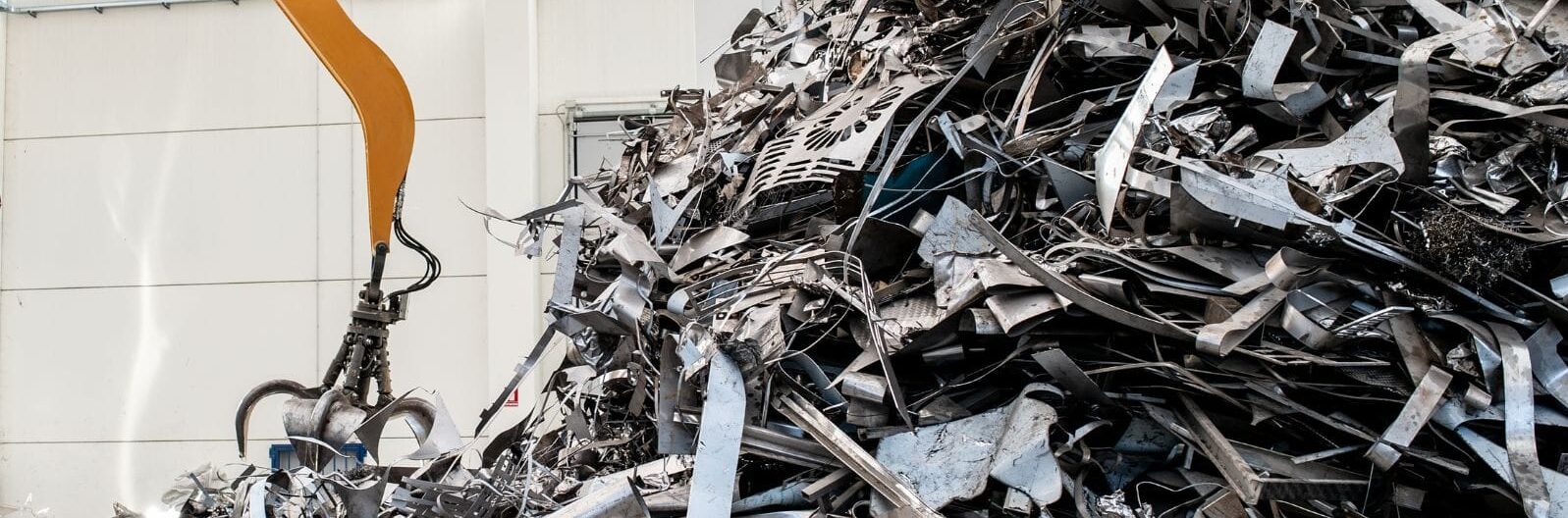

Τι είναι τα Βιομηχανικά Απόβλητα;
Τα βιομηχανικά απόβλητα περιλαμβάνουν ανεπιθύμητα υλικά που προκύπτουν από βιομηχανικές δραστηριότητες, όπως η μεταποίηση, η εξόρυξη, η παραγωγή ενέργειας και η επεξεργασία τροφίμων. Τα απόβλητα αυτά διαφέρουν από τα αστικά απόβλητα, τα οποία προέρχονται κυρίως από νοικοκυριά και επιχειρήσεις. Τα βιομηχανικά απόβλητα εμφανίζονται συνήθως σε μεγάλες ποσότητες και περιλαμβάνουν μια μεγάλη ποικιλία ουσιών. Ορισμένες από αυτές τις ουσίες μπορεί να είναι επικίνδυνες και να απαιτούν ειδικό χειρισμό.
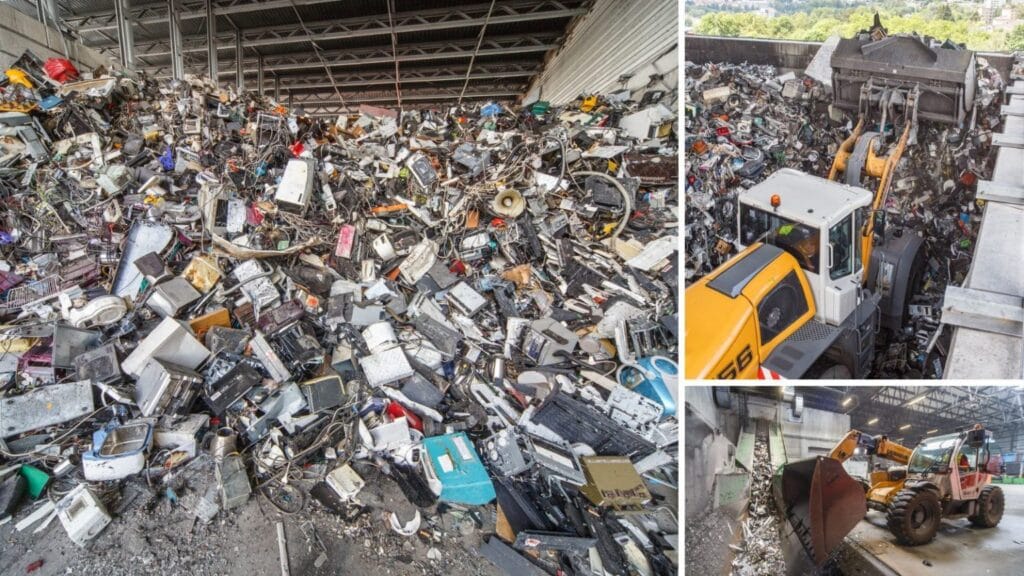

Κύριοι Τύποι Βιομηχανικών Αποβλήτων
Στερεά Απόβλητα:
Τα στερεά βιομηχανικά απόβλητα περιλαμβάνουν υλικά όπως παλιοσίδερα, πλαστικά, υλικά συσκευασίας, χαρτί, ιλύ (λάσπη) και δομικά μπάζα. Για παράδειγμα, μια μονάδα μεταλλικών κατασκευών παράγει ρινίσματα μετάλλου και υπολείμματα τεμαχίων ως στερεά απόβλητα.
Υγρά Απόβλητα:
Τα υγρά βιομηχανικά απόβλητα περιλαμβάνουν λύματα, έλαια, διαλύτες, οξέα και άλλες χημικές ουσίες που προκύπτουν από την παραγωγή ή τον καθαρισμό. Οι μονάδες παραγωγής ενέργειας και οι χημικές βιομηχανίες συχνά παράγουν μεγάλες ποσότητες υγρών αποβλήτων.
Επικίνδυνα Απόβλητα:
Τα επικίνδυνα απόβλητα περιέχουν υλικά που μπορούν να βλάψουν τον άνθρωπο ή το περιβάλλον. Παραδείγματα είναι τα βαρέα μέταλλα όπως ο μόλυβδος και ο υδράργυρος, οι διαλύτες, τα φυτοφάρμακα και ορισμένα παραπροϊόντα από την κατασκευή ηλεκτρονικών. Τα υλικά αυτά πρέπει να διαχειρίζονται και να απορρίπτονται με ιδιαίτερη προσοχή.
Μη Επικίνδυνα Απόβλητα:
Τα μη επικίνδυνα απόβλητα δεν δημιουργούν άμεσους κινδύνους. Σε αυτή την κατηγορία ανήκουν, για παράδειγμα, τα υπολείμματα τροφίμων από μονάδες επεξεργασίας τροφίμων και οι χάρτινες συσκευασίες από γραμμές συναρμολόγησης.
Χημικά Απόβλητα:
Τα χημικά απόβλητα προέρχονται από βιομηχανίες που χρησιμοποιούν ή παράγουν χημικές ουσίες. Περιλαμβάνουν χρησιμοποιημένους διαλύτες, οξέα, αλκάλια και αντιδραστικές ενώσεις. Κλάδοι όπως τα φαρμακευτικά προϊόντα, τα χρώματα και τα πλαστικά συμβάλλουν σημαντικά στην παραγωγή χημικών αποβλήτων.
Ηλεκτρονικά Απόβλητα (E-Waste):
Τα ηλεκτρονικά απόβλητα περιλαμβάνουν παλαιό εξοπλισμό, πλακέτες κυκλωμάτων και μπαταρίες από την κατασκευή ηλεκτρονικών συσκευών. Τα απόβλητα αυτά συχνά περιέχουν επικίνδυνα στοιχεία, αλλά μπορούν επίσης να περιέχουν πολύτιμα μέταλλα που είναι κατάλληλα για ανακύκλωση..

Κύριες Πηγές Βιομηχανικών Αποβλήτων
Οι κύριες πηγές βιομηχανικών αποβλήτων περιλαμβάνουν:
- Βιομηχανικές μονάδες παραγωγής: Παράγουν πολλούς τύπους αποβλήτων, όπως μεταλλικά υπολείμματα και χρησιμοποιημένους διαλύτες.
- Ενεργειακές μονάδες: Παράγουν τέφρα, ιλύ (λάσπη) και υπολειμματικές χημικές ουσίες.
- Επεξεργασία τροφίμων και ποτών: Οι διαδικασίες αυτές οδηγούν σε οργανικά απόβλητα, όπως φλούδες, πολτό και νερό πλύσης.
- Χημικές βιομηχανίες: Απελευθερώνουν κατάλοιπα, χρησιμοποιημένους διαλύτες και χημικές ουσίες διεργασιών.
- Κατασκευή ηλεκτρονικών: Οι δραστηριότητες αυτές δημιουργούν ηλεκτρονικά απόβλητα (e-waste), όπως ελαττωματικές πλακέτες κυκλωμάτων και χρησιμοποιημένες μπαταρίες.
Παράδειγμα:
Μια μονάδα μεταλλικών κατασκευών παράγει περισσότερους από έναν τύπους βιομηχανικών αποβλήτων. Παράγει παλιοσίδερα, τα οποία αποτελούν μορφή στερεών αποβλήτων, και χρησιμοποιεί επίσης διαλύτες που κατά τη διάρκεια της παραγωγής μετατρέπονται σε επικίνδυνα υγρά απόβλητα.
Όπως φαίνεται, τα βιομηχανικά απόβλητα εμφανίζονται σε πολλές μορφές και προέρχονται από πολλές διαφορετικές πηγές. Κάθε τύπος απαιτεί ειδική διαχείριση ώστε να αντιμετωπίζεται με ασφάλεια και υπευθυνότητα.

Περιβαλλοντικές και Κοινωνικές Επιπτώσεις: Κίνδυνοι για τα Οικοσυστήματα και τη Δημόσια Υγεία
Μόλυνση των Φυσικών Πόρων
Όταν οι βιομηχανίες δεν διαχειρίζονται σωστά τα απόβλητα, το έδαφος, το νερό και ο αέρας μπορούν να ρυπανθούν. Επικίνδυνες χημικές ουσίες, όπως βαρέα μέταλλα, διαλύτες και επίμονοι οργανικοί ρύποι, συχνά διαρρέουν από χώρους απόθεσης αποβλήτων προς τα υπόγεια ύδατα και τα ποτάμια. Αυτή η διαδικασία μπορεί να βλάψει τα υδάτινα οικοσυστήματα και να καταστήσει το πόσιμο νερό μη ασφαλές. Επιστημονικές έρευνες δείχνουν ότι τα βιομηχανικά απόβλητα μπορούν να αυξήσουν τη συγκέντρωση τοξικών ουσιών στα τοπικά υδάτινα συστήματα. Οι τοξίνες αυτές μπορούν να διαταράξουν την υδρόβια ζωή και να μειώσουν τη βιοποικιλότητα της περιοχής. Για παράδειγμα, αν διαλύτες και βαρέα μέταλλα από εργοστάσια εισέλθουν στα υπόγεια ύδατα, το νερό αυτό μπορεί να μην είναι πλέον ασφαλές για πόση ή για χρήση στη γεωργία.
Ποιότητα του Αέρα και Τοξικές Εκπομπές
Τα βιομηχανικά απόβλητα μπορούν να απελευθερώνουν ρύπους στον αέρα, συμπεριλαμβανομένων πτητικών οργανικών ενώσεων και μικροσκοπικών στερεών σωματιδίων που ονομάζονται αιωρούμενα σωματίδια. Οι ρύποι αυτοί μπορούν να διασπείρονται σε μεγάλες αποστάσεις, επηρεάζοντας ανθρώπους που ζουν μακριά από την αρχική πηγή. Η μακροχρόνια εισπνοή αυτών των ουσιών μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε αναπνευστικές παθήσεις, προβλήματα στο καρδιαγγειακό σύστημα και αυξημένο κίνδυνο εμφάνισης καρκίνου, ιδιαίτερα για όσους ζουν κοντά σε βιομηχανικές εγκαταστάσεις.
Κίνδυνοι για τη Δημόσια Υγεία στις Γειτονικές Κοινότητες
Οι άνθρωποι που ζουν κοντά σε βιομηχανικές περιοχές αντιμετωπίζουν αυξημένους κινδύνους για την υγεία, επειδή εκτίθενται σε μολυσμένο αέρα, νερό και έδαφος. Μελέτες δείχνουν ότι σε αυτές τις κοινότητες παρατηρούνται περισσότερα περιστατικά αναπνευστικών λοιμώξεων, δερματικών προβλημάτων και αναπτυξιακών διαταραχών, ιδιαίτερα μεταξύ των παιδιών και των ατόμων που είναι πιο ευαίσθητα σε τοξικές ουσίες.
Παράδειγμα από την Πραγματική Ζωή
Σε μια καταγεγραμμένη περίπτωση, μια μονάδα παραγωγής απέθεσε διαλύτες με λανθασμένο τρόπο, γεγονός που προκάλεσε μόλυνση των υπόγειων υδάτων στη γειτονική κοινότητα. Οι κάτοικοι παρουσίασαν αυξημένα περιστατικά ασθενειών και οι τοπικές αρχές αναγκάστηκαν να προμηθεύσουν καθαρό νερό για να αποτρέψουν περαιτέρω προβλήματα υγείας.
Η σωστή διαχείριση των βιομηχανικών αποβλήτων συμβάλλει στην προστασία των τοπικών οικοσυστημάτων και στη διατήρηση της ασφάλειας των κοινοτήτων από αυτούς τους γνωστούς κινδύνους.

Ποσοτικοποίηση Αποβλήτων και Αναφορά Δεδομένων: Ποσοτική Εκτίμηση και Παρακολούθηση της Παραγωγής Αποβλήτων
Μέτρηση Βιομηχανικών Αποβλήτων
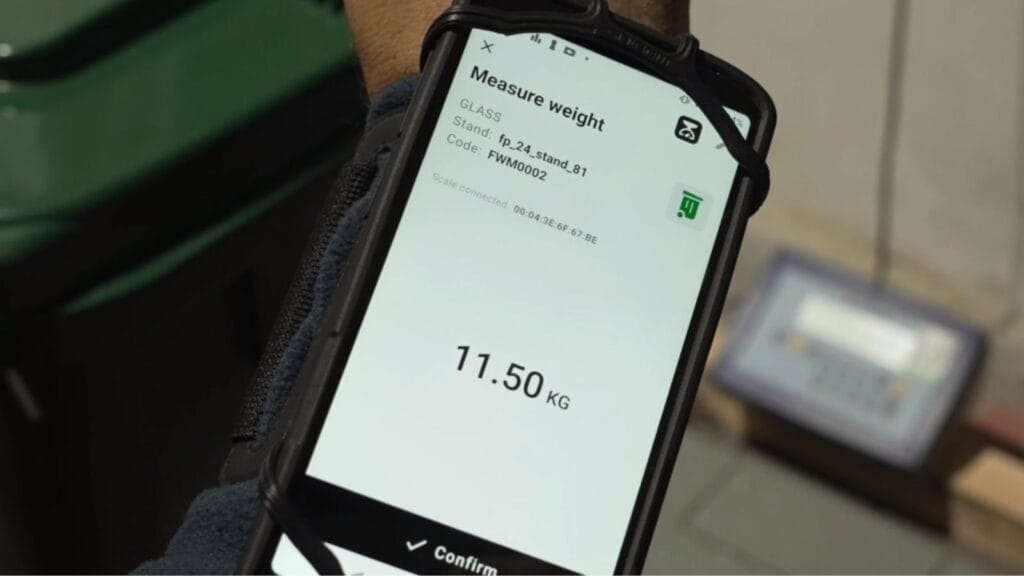
Για να διαχειριστείτε αποτελεσματικά τα βιομηχανικά απόβλητα, πρέπει πρώτα να τα μετρήσετε με ακρίβεια. Όταν γνωρίζετε πόσα απόβλητα παράγει το εργοστάσιό σας, μπορείτε να συμμορφώνεστε με τους περιβαλλοντικούς κανονισμούς, να θέτετε στόχους για τη μείωση των αποβλήτων και να εντοπίζετε τρόπους βελτίωσης των παραγωγικών διαδικασιών. Αν δεν συλλέγετε αξιόπιστα δεδομένα, δεν μπορείτε να αξιολογήσετε αν οι προσπάθειές σας αποδίδουν ούτε να αποδείξετε ότι τηρείτε τους κανονισμούς.
Πώς να Μετρήσετε την Παραγωγή Αποβλήτων
Μπορείτε να χρησιμοποιείτε άμεσες και έμμεσες μεθόδους για τη μέτρηση των βιομηχανικών αποβλήτων. Οι άμεσες μέθοδοι περιλαμβάνουν τη ζύγιση των αποβλήτων κατά την παραγωγή τους, τη χρήση δαπέδιων ζυγών για στερεά υλικά ή παροχόμετρων για υγρά. Οι έμμεσες μέθοδοι εκτιμούν τα απόβλητα εξετάζοντας την ποσότητα των πρώτων υλών που χρησιμοποιούνται, την τελική παραγωγή ή πρότυπα από ιστορικά δεδομένα. Μπορείτε να χρησιμοποιείτε έμμεσες μεθόδους όταν η άμεση μέτρηση είναι πολύ δύσκολη.
Όταν πρόκειται για επικίνδυνα απόβλητα, πρέπει να τηρούνται αυστηροί νόμοι. Για παράδειγμα, ο αμερικανικός νόμος Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) απαιτεί την τήρηση ακριβών αρχείων σχετικά με τον τύπο, την ποσότητα και τον τρόπο διαχείρισης κάθε ρεύματος επικίνδυνων αποβλήτων.
Συλλογή και Αναφορά Δεδομένων Αποβλήτων
Τα εργοστάσια συλλέγουν δεδομένα αποβλήτων με διαφορετικούς τρόπους. Ορισμένα χρησιμοποιούν χειρόγραφα ημερολόγια ή υπολογιστικά φύλλα, ενώ άλλα επιλέγουν ψηφιακά εργαλεία. Τα αυτοματοποιημένα συστήματα, όπως κάδοι με γραμμωτό κώδικα, αισθητήρες ροής και γεφυροπλάστιγγες, μπορούν να καταγράφουν δεδομένα άμεσα και να μειώνουν τα λάθη. Τα εργοστάσια συνήθως συγκεντρώνουν αυτές τις πληροφορίες σε μηνιαίες ή τριμηνιαίες αναφορές. Οι αναφορές αυτές τα βοηθούν να συμμορφώνονται με τους τοπικούς κανονισμούς και να καθοδηγούν τις δικές τους προσπάθειες για πιο υπεύθυνη χρήση των πόρων.
Staying Compliant and Improving Over Time
Regulations tell factories how and when to report waste data. Detailed records help track waste from its source and make audits easier. When you monitor waste regularly, you can compare your performance over time, find ways to save money, and focus on cutting waste where it matters most.
Example: How a Factory Tracks and Reduces Waste
A manufacturing plant uses digital forms and floor sensors to record the amount of waste each department creates every day. At the end of each month, staff review this data to prepare compliance reports and to spot problems, like too much packaging or steps in the process that create extra waste. This routine helps the factory meet legal requirements and make progress toward its environmental goals.
When you set up clear systems for measuring and reporting waste, you give your facility the tools it needs to manage waste better and keep improving how it operates.
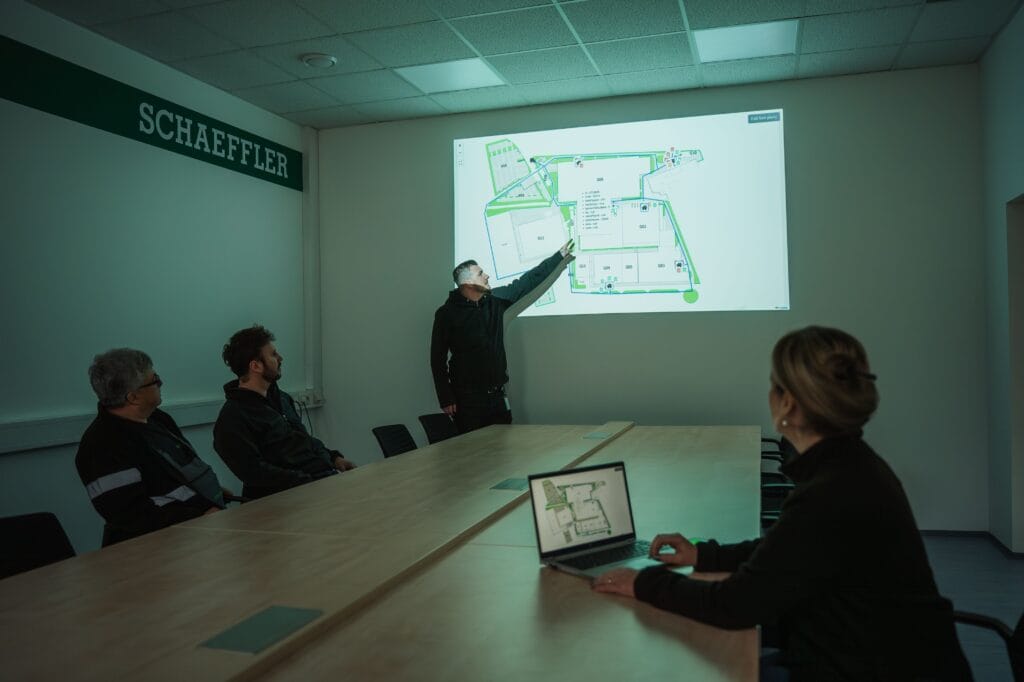

Waste Diversion and Sorting: Maximizing Diversion and Reducing Contamination
Waste Diversion Rate
Waste diversion rate measures how much waste you keep out of landfills by recycling, composting, or reusing materials. You can calculate this rate using the formula:
Waste Diversion Rate (%) = (Weight of Diverted Waste / Total Waste Generated) × 100
For example, scientific research shows that effective waste diversion in industrial settings can lower landfill disposal by more than 60%. This reduction helps limit environmental harm and meets sustainability targets.
Sorting Processes: Manual, Automated, and Centralized Systems
Sorting waste correctly helps you increase your diversion rate. Industrial facilities use several methods to sort waste:
- Manual Sorting: Workers separate waste at the source or at special sorting stations. This method lets you identify items quickly, but you need to train staff regularly and monitor the process closely.
- Automated Sorting: Machines like conveyor belts, optical sorters, and magnetic separators sort metals, plastics, and electronics. These tools help increase sorting speed and accuracy.
- On-site vs. Centralized Sorting: On-site sorting lets you divert waste immediately. Centralized sorting uses advanced equipment to manage complex waste streams, which often increases the amount of material you can recover.
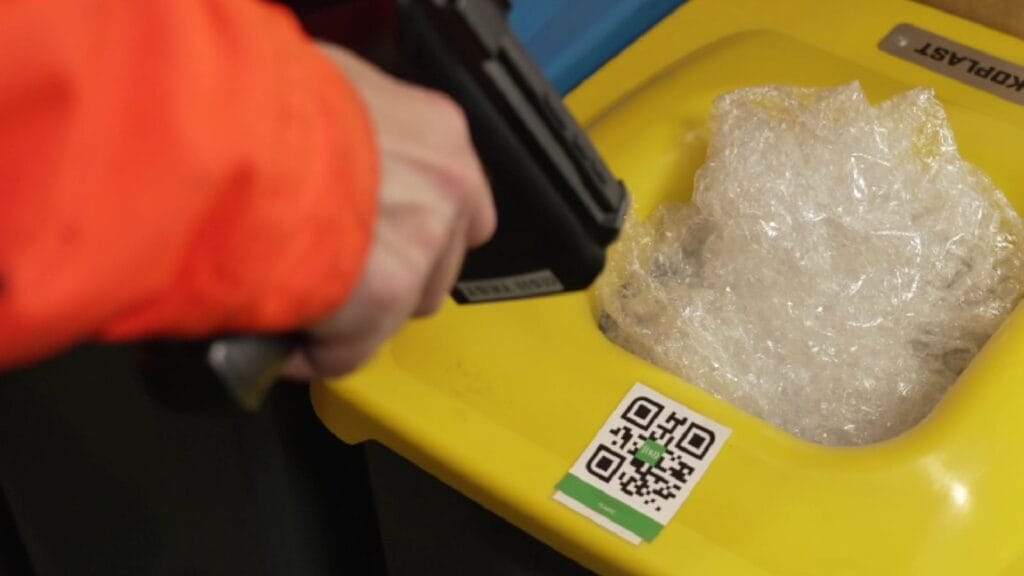

How Proper Sorting Affects Diversion
When you separate recyclables (like metals and plastics), compostables (such as food scraps), and items that can be reused from landfill waste, you can reach higher diversion rates. Industry data shows that strong sorting systems can help you divert 50–70% of your waste. For instance, a factory might recycle metal scraps, compost cafeteria waste, and reuse packaging, achieving a 60% diversion rate.
Contamination: Causes and Results
Contamination happens if you mix incompatible materials, such as hazardous chemicals with recyclables. Even small amounts of contamination can make recyclable materials unusable. This can lead to more landfill disposal and may break environmental laws.
Examples of contamination in industrial settings include:
- Putting oily rags with paper waste
- Mixing hazardous chemical residues with clean recyclables
- Throwing away electronic parts with general waste
Ways to Reduce Contamination
To recycle efficiently and follow regulations, you need to control contamination. These steps can help:
- Staff Training: Teach employees how to separate waste properly. Regular training reduces mistakes and increases the amount of waste you can divert.
- Clear Labeling: Use color-coded bins and clear signs. This helps everyone know where to put each type of waste.
- Process Improvements: Set up clear procedures and do regular checks. This keeps sorting consistent and helps you find ways to improve.
Many factories that combine these methods have reached diversion rates above 60%, as shown in studies and industry reports.
Example:
A manufacturer manages to divert 60% of its waste by recycling metal shavings and composting cafeteria scraps. The company trains staff often and uses clear labels on bins, which keeps oily rags out of the paper recycling and helps keep streams clean.
Boosting Operational Efficiency: Streamlining Waste Handling Processes
Enhancing Productivity Through Efficient Waste Management
Industrial waste management affects how well manufacturing operations run and how much they cost. When you streamline waste handling, you help prevent delays and keep production moving smoothly. Managing waste efficiently also helps companies follow environmental laws and lowers risks during operations.
Key Strategies for Process Optimization
1. Process Optimization and Source Reduction
You can make your manufacturing processes more efficient by reducing waste at the source. This includes changing how you use raw materials, upgrading equipment, and using better control systems. These steps lower the amount of waste you produce and make it easier to handle what remains. For example, if you replace hazardous materials with safer options or switch from organic solvents to water-based ones, you decrease how much waste you need to treat.
2. Coordinated Collection and Storage
When you match waste collection times with your production schedule, you avoid overflow and cut down on unnecessary delays. This kind of scheduling removes waste before it piles up, helps keep the workplace safe, and limits the chances of environmental problems. Good storage methods, like using clearly labeled bins and keeping different waste types separate, make collection and handling faster and more accurate.
3. Route and Logistics Optimization
If you plan and improve the routes for moving waste inside your facility, you can cut down on transport time and need less labor. Research shows that having dedicated pathways for waste and reducing traffic in these areas lowers costs and reduces the risk of accidental mixing or spills.
Benefits of Streamlined Waste Handling
When you set up efficient waste handling procedures, you save time and resources during collection, transport, and storage. This efficiency also helps you avoid breaking regulations because waste is removed properly and on schedule. Plants that plan waste collection around their production activities usually face fewer shutdowns and meet environmental standards more consistently.
Example:
A factory schedules waste pickup right after its busiest production shifts. This prevents containers from overflowing and reduces unplanned stoppages. As a result, the factory has seen lower disposal costs and improved compliance with regulations.
By managing industrial waste effectively, you can help your factory or plant run more smoothly and meet modern production goals.

Smart Waste Management and IoT Solutions: Implementing Automation and Real-Time Monitoring
Harnessing IoT for Intelligent Waste Management
You can use Internet of Things (IoT) technology to make industrial waste management more efficient. IoT systems use devices like fill-level sensors, RFID tags, and wireless transmitters. These devices monitor waste containers and collection points across a facility. Sensors collect data on how full each bin is, as well as temperature and gas emissions. This information updates in real time, so facility managers always know the current status of waste collection areas.
Automation and Real-Time Insights
Automated waste systems connect IoT devices to a central dashboard. This setup lets managers see waste build-up patterns as they happen. When a container gets close to full, fill-level sensors send out alerts. This helps managers schedule pickups only when needed, which means fewer unnecessary trips for waste collection. According to a 2024 study in Scientific Reports (Nature), IoT-based systems can cut waste collection trips by up to 40%. This reduces both fuel use and operating costs.
Benefits of Smart Solutions
Smart waste management brings several advantages to industrial settings:
- Lower Labor and Maintenance Needs: Automated messages mean staff do not have to check bins manually. Workers can spend more time on other important tasks.
- Prevention of Spills and Overflows: Alerts arrive before containers overflow, which helps prevent spills and reduces safety risks.
- Better Compliance: Real-time tracking makes it easier to keep precise records for environmental reports and audits.
- Efficient Resource Use: Data from sensors allows facilities to adjust collection routes, choose the best spots for bins, and plan maintenance more accurately.
Example Application
Imagine a manufacturing plant using bins fitted with fill-level sensors and wireless transmitters. When a bin gets close to being full, the system sends a notice directly to staff. This process helps workers collect waste before it overflows, keeps the facility within safety guidelines, and improves waste management efficiency—all without needing to check bins by hand.
This section explains how facilities can use technology to automate waste collection, monitor containers in real time, and improve the entire waste management process.
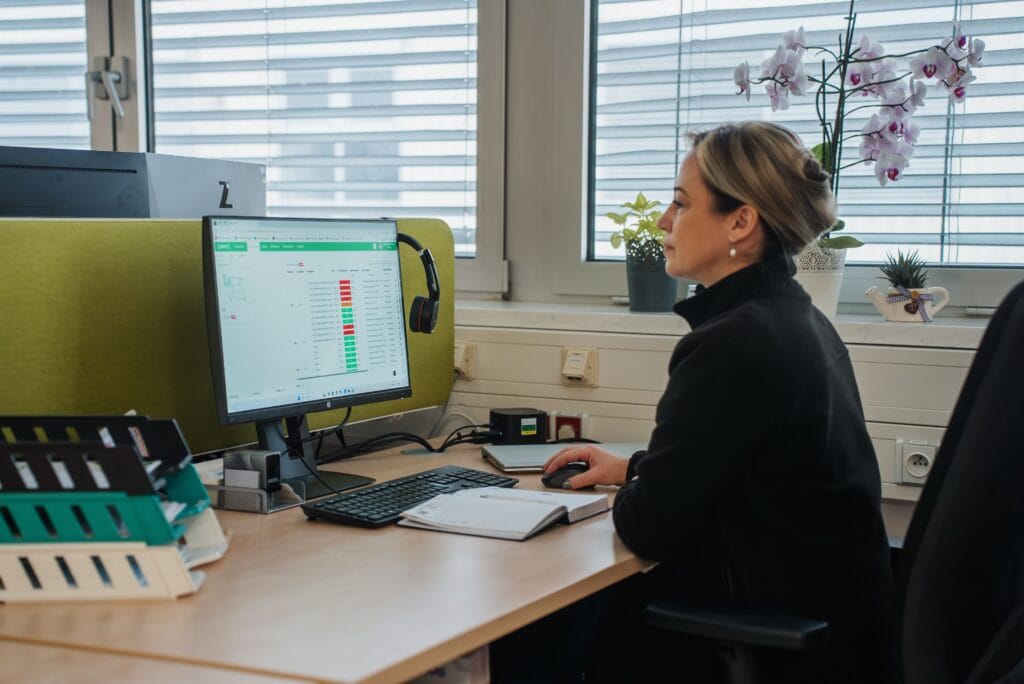

Data-Driven Approaches and Future Innovations: Leveraging Analytics, AI, and Emerging Technologies
Advanced Analytics for Informed Decision-Making
Today, industrial waste management uses advanced data analytics to guide daily decisions and support sustainability efforts. When you collect data from production lines, waste streams, and disposal processes, you can apply statistical modeling and machine learning. These tools help you predict how much waste a factory will produce, find where resources are being used poorly, and improve how resources get allocated. For example, predictive models use past production data to estimate when waste levels might peak. This lets you adjust production schedules or processes in advance so you can reduce waste and avoid expensive overflows.
Artificial Intelligence and Automated Sorting
Artificial intelligence (AI) brings automation to waste management through advanced sorting systems and real-time waste classification. Machine vision and AI-powered robots sort items on conveyor belts by type, such as recyclable, hazardous, or non-recyclable materials. This process keeps contamination low and helps more waste get recycled. AI systems learn from the data they gather during daily operations, so they keep improving sorting accuracy and can adapt as waste streams change.
Integration with Sustainability and ESG Goals
Data-driven methods help facilities connect waste management with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals. You can use analytics dashboards to monitor key performance indicators, including how much waste is diverted from landfills, the facility’s carbon footprint, and compliance with regulations. These tools make it easy to report progress clearly to stakeholders and regulators. They also let you compare your facility’s performance to industry standards.
Future-Ready Technologies: Blockchain and Circular Economy Models
New technologies continue to change industrial waste management. Blockchain platforms provide secure and transparent tracking for waste streams. With blockchain, you can follow waste from its source all the way to disposal or recycling. This process limits illegal dumping and inaccurate reporting. Digital platforms that support circular economy models encourage you to reuse and regenerate materials. This approach shifts away from the old linear model of disposal and instead supports sustainable cycles for resources.
Example:
A factory uses predictive analytics to spot when waste surges will happen before major maintenance events. With this information, the factory can change its production and waste handling plans ahead of time. This approach leads to lower waste levels and helps the factory stay within environmental guidelines.
Latest waste library articles

Ο Ρόλος της ΕΥΣ στην Διαχείριση Αποβλήτων και την Εξέλιξη Πολιτικής στις ΗΠΑ
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
6 εκπληκτικά στατιστικά στοιχεία για το Σχέδιο Επιστροφής Καταθέσεων (DRS) που πρέπει να γνωρίζετε.
Deposit Return System
Η Εξέλιξη της Συμμόρφωσης με την EPR και των Συστήματων Λογισμικού PRO
EPR Compliance, Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Επισκόπηση και αποτελέσματα των Συστημάτων Επιστροφής Εγγύησης στην Ευρώπη
Έξυπνο Δελτίο Αποβλήτων
Λάβετε μηνιαίες ενημερώσεις από την εταιρεία μας και από τον κόσμο της διαχείρισης αποβλήτων!








